Operating Leverage: Introduction, Method and Degree
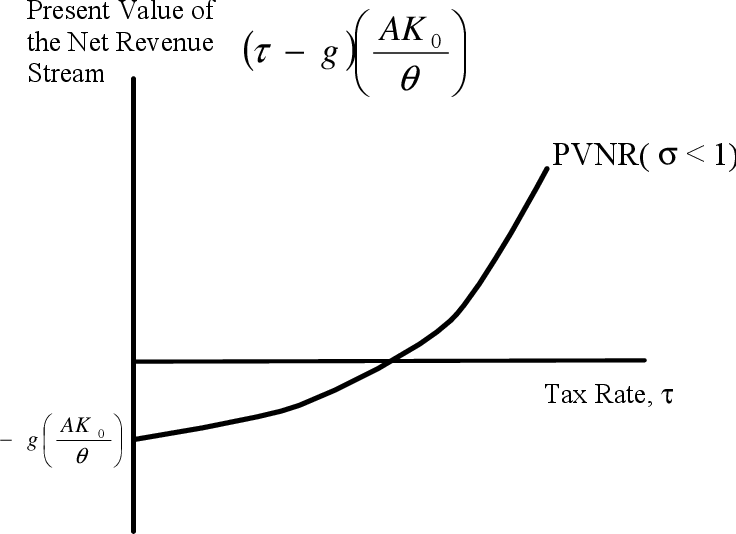
The purpose of this paper is to derive the optimal DOL (degree of operating leverage) of a company with flexibility in investment and production. The choice of DOL is a critical one because it impacts the company’s risk level, operating and financial performance, and valuation. However, there is virtually no research on how a company should choose its DOL. With a wide range of input parameter values, our model generates optimal DOL figures that are similar in magnitude to empirical estimates. We also identify the important determinants of DOL, such as costs (fixed cost, variable cost, and cost of capacity), demand characteristics (growth rate, volatility, and price-sensitivity), productivity of capital, and interest rate.
This allows investors to estimate profitability under a range of scenarios. As stated above, in good times, high operating leverage can supercharge profit. But companies with a lot of costs tied up in machinery, plants, real estate and distribution networks can’t easily cut expenses to adjust to a change in demand. So, if there is a downturn in the economy, earnings don’t just fall, they can plummet. Running a business incurs a lot of costs, and not all these costs are variable.
Difference between Operating Leverage and Financial Leverage Accounting
In evaluating the wisdom of their investment in a corporation, its owners
should use the current market value of its stock, because this is what they would have
available to invest elsewhere if they liquidated the stock. This team of experts helps Finance Strategists maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible. The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice. All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly.
What does operating leverage depend on of a firm?
Significance. Operating leverage calculation measures the company's fixed costs as a percentage of its total costs. Therefore, a company with a higher fixed cost will have high operating leverage than a higher variable cost.
Therefore, what is missing in the literature is a comprehensive model that determines DOL in a joint production/investment framework. Moreover, we also consider the effect of demand behavior and uncertainty (which impact DOL via the output price and quantity choices), by means of a stochastic downward-sloping demand function. Kumar and Yerramilli (2016) examine the relationship between operating and financial leverage, using a real-option model where the firm jointly identifies optimal capacity and optimal leverage ratio. They show that optimal DOL is an increasing function of cash flow volatility if the cost of subsequent expansion is high enough. However, their DOL is completely determined by capacity (in fact, capacity is treated as interchangeable with DOL), hence the other determinants of DOL are ignored.
Irreversibility and aggregate investment
It is widely recognized that the DOL has a significant impact on a company’s operating and financial policies and performance, thus it is necessary to choose the DOL judiciously. However, the existing literature focuses on the effects of DOL, and not on the choice of DOL. While a few papers have studied the firm’s DOL choice, they ignore either the investment (capacity and timing) decision or the production (output level) decisions, both of which are crucial in determining the DOL. Unfortunately, unless you are a company insider, it can be very difficult to acquire all of the information necessary to measure a company’s DOL. Consider, for instance, fixed and variable costs, which are critical inputs for understanding operating leverage. It would be surprising if companies didn’t have this kind of information on cost structure, but companies are not required to disclose such information in published accounts.
In this article, we’ll give you a detailed guide to understanding operating leverage. Generating this type of cost information is very different than the requirements of GAAP. Accountants try to create management information that links to GAAP; but since cause and effect is not a GAAP principle, the effort is doomed to fail. The only way to generate causal information on the nature of costs is to apply resource consumption accounting or a German management accounting method known as grenzplankostenrechnung (GPK for short). Activity-based costing has a tendency to make all costs appear variable and should be used with caution to ensure the fixed and variable nature of costs are accurately reflected. In spite of its importance, there is surprisingly little research on how a firm should decide on its DOL; in other words, what is the company’s “optimal” DOL?
Why You Can Trust Finance Strategists
Owners’ return rises by 9.33 percent as a result of the financial
leverage obtained by 70 percent debt financing at a cost of 8 percent. If borrowing rose
above 70 percent, this figure would rise, that is, financial leverage would be greater. If
financial leverage is measured, instead, as an index number, an additional calculation is
necessary to determine what return on equity it produces. Businesses change the level of output in order increase the rate of return
enjoyed by their owners. This can be done either by selling more units or avoiding
producing units which cannot be sold without a rate-of-return-reducing reduction in price.
- Shown in Tables
1 and 2 (below) are their revenues and costs for the production of up to 25,000 units of
output. - The value of this ratio is greater the lower is the ratio of variable cost
per unit to price per unit; so, the greater is this ratio, the higher is operating
leverage. - Insourcing provides the options to reduce the fixed cost structure (the reduce FC option), reduce the variable costs (the reduce VC option), or reduce both through process improvement, innovation and investment.
- The management of ABC Corp. wants to determine the company’s current degree of operating leverage.
- Higher DOL means higher operating profits (positive DOL), and negative DOL means operating loss.
This information shows that at the present level of operating sales (200 units), the change from this level has a DOL of 6 times. This variation of one time or six-time (the above example) is known as degree of operating leverage (DOL). It is also useful to frame this as the operating margin, which compares the overall revenue to the overall
operating income.
Similar to Types of Leverage(
As sales took a nosedive, profits swung dramatically to a staggering $58 million loss in Q1 of 2001—plunging down from the $1 million profit the company had enjoyed in Q1 of 2000. During the 1990s, investors marveled at the nature of its software business. The company spent tens of millions of dollars to develop each of its digital delivery and storage software programs. But thanks to the internet, Inktomi’s software could be distributed to customers at almost no cost.
However, increasing operating leverage can also cause substantial losses
and puts more pressure on a business. The key to understanding the appropriate amount of operating
leverage lies in the analysis of the break-even point. In finance, companies assess their business risk by capturing a variety of factors that may result in lower-than-anticipated profits or losses. One of the most important factors that affect a company’s business risk is operating leverage; it occurs when a company must incur fixed costs during the production of its goods and services.
Fixed costs do not vary with the volume of sales, whereas variable costs vary directly with sales volume. When sales have exceeded the break-even point, a larger contribution margin will mean greater increases in
profits for a company. By inserting different prices into the break-even formula, you will obtain a number of
break-even points – one for each possible price charged. The value of this ratio is greater the lower is the ratio of variable cost
per unit to price per unit; so, the greater is this ratio, the higher is operating
leverage. Block and Hirt’s method produces the
same results when operating leverage is computed at the 10,000 unit level of output. Although you need to be careful when looking at operating leverage, it can tell you a lot about a company and its future profitability, and the level of risk it offers to investors.
More sensitive operating leverage is considered riskier since it implies that current profit margins are less secure moving into the future. Unit contribution margin can be thought of as the fraction of sales, or the amount of each unit sold, that
contributes to the offset of fixed costs. Operating leverage exists when a firm has to pay fixed cost irrespective of volume of output or sales. operating leverage arises because of An even more extreme case is produced by letting Widget Works, Inc. have
fixed costs of $10,000 and variable costs per unit of $1.00, while Bridget Brothers has
fixed costs of only $100 and variable cost per unit of $1.99. Observe that now Widget
Works’ fixed costs are 100 times Bridget Brothers’, and that its variable costs
are just barely over one-half of Bridget Brothers’.
What does operating leverage depend on of a firm?
Significance. Operating leverage calculation measures the company's fixed costs as a percentage of its total costs. Therefore, a company with a higher fixed cost will have high operating leverage than a higher variable cost.
- Published in Forex Trading
What Are Bullish And Bearish Harami Candles?

Sometimes a pattern that’s formed with high volatility is more reliable than one that’s formed in low volatility conditions. What works best depends on the market and timeframe you’re trading, and you should test and see what works the best for you. For example, in some markets one day of the week or one-third of the month might be extra bullish or bearish. During the rest of the day selling pressure tries to push the market lower, but buyers are there each time to prevent the market from heading lower.
All in all, the bullish harami pattern is a sign that bulls managed to not only make the market gap to the upside, but also hold that level for the rest of the day. To some, a line drawn around this pattern resembles a pregnant woman. A bullish harami is a basic candlestick chart pattern indicating that a bearish trend in an asset or market may be reversing. Ideally, to increase the accuracy, we want to trade the Bullish Harami candlestick pattern by combining it with other types of technical analysis or indicators. Without all these additional pieces of information, it is too risky to depend solely on this one pattern to take a position. In an engulfing pattern, the two candles should have opposite colors.
Which candlestick pattern is most bullish?
A probable trade set up can be initiated if the third candle crosses the 1st candles’s low keeping stoploss at the 1st candle’s high. The real body of the candle on Day 2 will be well within the real body of Day 1 candle. The 1st candle will always be the colour of the prior trend and the second candle will be the reversal candle. Just like the hammer, experienced traders usually wait for confirmation of an uptrend from the next candle before making their move. For example, in a 15-min chart, a candle represents the price movements of the security within 15 minutes.
Trading the Bullish Harami Pattern – DailyFX
Trading the Bullish Harami Pattern.
Posted: Thu, 04 Jul 2019 07:00:00 GMT [source]
The Bullish Harami Cross also provides an attractive risk to reward potential as the bullish move (once confirmed) is only just starting. A candlestick chart typically represents the price data of stock on a single day, including opening price, closing price, high price, and low price. A Bearish Harami is formed when there is a large bullish candle on Day 1 and bullish harami candle is followed by a smaller bearish candle on Day 2. An important aspect of the bearish Harami is that prices should gap down on Day 2. The short shadows (wicks) and consecutive higher closes indicate that buyers are able to sustain the uptrend. The strength of the buying pressure is also confirmed by the large size of the candles which are usually the same size.
Trading Harami with Price Action:
Some traders may use candlestick patterns to understand market trends and plan entry or exit points. Bullish harami candlesticks can be a part of a larger pattern such as symmetrical triangle patterns. Smaller 2 day patterns like the bullish harami may not always form a significant reversal; doji candlesticks can form after the initial pattern sometimes creating confusion.

If the second candle is a doji, it is called a bullish harami cross. HowToTrade.com helps traders of all levels learn how to trade the financial markets. The figure presents that the biggest “problem” of the harami patterns is their first candle. On the chart, we can see that the market could not win with the Black Candle being the first line of the Bullish Harami pattern.
The Bullish Harami Candlestick Pattern – Pros and Cons
If you would like to contact the Bullish Bears team then please email us at bbteam[@]bullishbears.com and we will get back to you within 24 hours. The opposite of the Bullish Harami is the Bearish Harami and is found at the top of an uptrend. It’s worth comparing the Harami patterns to the somewhat opposite Bearish Engulfing Pattern and the Bullish Engulfing Pattern.
If you get a confirmation, this should trigger a sell signal which could be a sign for investors to pull out of the market. The stock is in a downtrend but is pregnant with a bullish reversal. When the bullish harami candle forms, the birth happens and the trend changes. A Bullish Harami candlestick is formed when a large bearish red candle appears on Day 1 that is followed by a smaller bearish candle on the next day.
Performance On All 75 Candlestick Pattern
If you are day trading, the Daily Pivot Points are the most popular, although the Weekly and Monthly are frequently used too. It’s simple, the Bullish Harami pattern is traded when the high of the last candle is broken. A Bullish Harami appearing after this bearish move is a sign of a possible reversal to the upside. When https://g-markets.net/ trading the Bullish Harami, we want to see the price first going down, making a bearish move. The pattern is bullish because we expect to have a bull move after the Bullish Harami appears at the right location. The price continued lower for a couple of weeks before reversing and then breaking above the resistance level.
- This means without any indicators, oscillators or moving averages, etc.
- People come here to learn, hang out, practice, trade stocks, and more.
- There are two types of Harami candlestick patterns – the Bearish Harami pattern and the Bullish Harami pattern.
Since the Bullish Harami appears at the start of a potential uptrend, traders can include multiple target levels to ride out a new extended uptrend. These targets can be placed at recent levels of support and resistance. The Harami Candlestick Pattern is considered a trend reversal pattern that can either be bullish or bearish, depending on the direction of the price action.
Bullish Harami Pattern
One should note that the important aspect of the bullish Harami is that prices should gap up on Day 2. Unique to Barchart.com, data tables contain an option that allows you to see more data for the symbol without leaving the page. Click the “+” icon in the first column (on the left) to view more data for the selected symbol. Scroll through widgets of the different content available for the symbol.
Bearish Harami: Definition and Trading Strategies – Investopedia
Bearish Harami: Definition and Trading Strategies.
Posted: Sun, 26 Mar 2017 06:38:27 GMT [source]
The hammer is a bullish candlestick pattern that indicates when a security is about to reverse upwards. The hammer is characterized by a small-bodied candle with a long shadow (wick). It is named “hammer” because it looks like a hammer with a long handle. The data shows us that the patterns likely mean volatility is incoming and that traders should go against the grain and listen to the data instead of trading like everyone else. The bullish harami is traded optimally using a bullish mean reversion strategy in the stock market and a bearish mean reversion trading strategy in the crypto and forex markets.
It is important to wait for a clear direction; sometimes a stock can just chop around and consolidate in an area for a bit as it is figuring out where to go. This pattern is often seen as a sign of indecision or uncertainty in the market. The first candle shows a strong move in one direction (downward in this case), followed by the second candle’s smaller body and lack of a clear path. If the trend reverses and starts moving upwards after a bullish harami pattern appears, it could be a sign that the bulls (buyers) are beginning to regain market control. The appearance of the doji after the first bearish candle indicates indecision between buyers and sellers. The trend is confirmed by the third smaller candlestick, which is either bearish or bullish.
- Published in Forex Trading